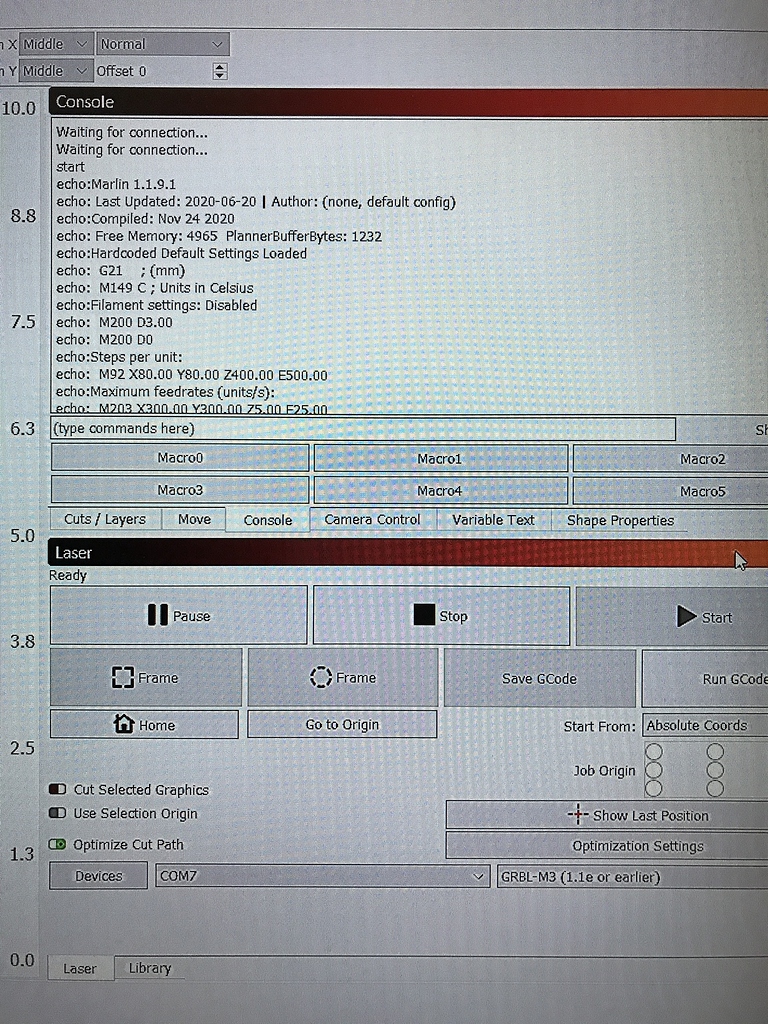
Manual Control When you turn your printer on, you will often come to this tab. The above picture shows the tab after connecting with the printer. In the first row you can set debug options for the printer. Repetier-Host is a free all-in-one 3D printing software solution that works with almost all popular FDM 3D printers, with over 500,000 installations. It has multi-slicer support, multi-extruder support, easy multi-printing, full control over your printer, and access from anywhere via browser. The Repetier-Host is a simple to use host software, which is be compatible with most firmwares around. You can add and position your STL files on the simulated printbed and slice them all together. For slicing you can use the built-in Slic3r slicer or use the well-known Skeinforge. I just finished my first MPCNC build and am having trouble with testing it via manual control in Repetier-Host. When I plug my board into the wall and my computer, I have no trouble connecting. However, when I click a manual control option, nothing happens. My baud rate is set to 250000 and I have the latest firmware flashed (I think.). After opening Repetier and connecting your 3D printer, select the manual control tab. SourceForge ranks the best alternatives to Repetier-Host in 2020. It simply stacks commands. Click “Printer Settings” and create a new profile by typing the name in the Printer field and configure the profile as below.
Repetier Manual Control Macbook Pro
If you have a 3d printer, you need to feed it with data. The typical workflow is as follows:
Repetier Manual Control Macbook

- Create a 3d model and export it in stl format or get it from the internet.
- Arrange one or more models on a virtual print plate.
- Slice the the models into thin slices and compute a path for printer head. This is done by a slicing software, which converts the model into g-code, the language your printer speaks.
- Check the created g-code for errors and printability.
- Send the g-code to your printer or copy the code to a sd card, which you can insert into your printer.
- Monitor your printer.
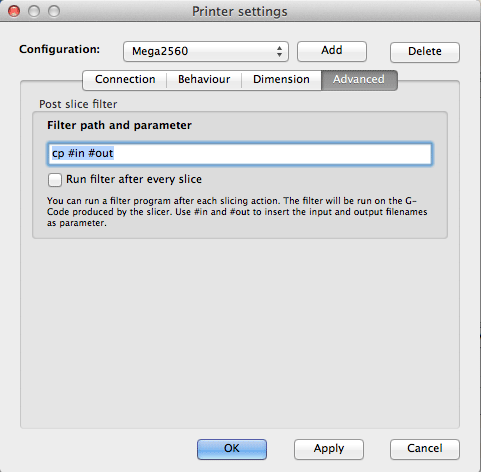
Except for point 1 the host offers everything you need. As you will see, the host interface offers different tabs to guide you easily through the workflow.
